HVAC Services
Get Professional Repairs From The Area's Trusted HVAC Technicians. Ask About Our Services! We Offer Professional Heating & Cooling System Repairs And Guarantee Long-Lasting Results.
Got Question? Call us: (850) 678-2665Financing
Commercial Vs. Residential HVAC: Key Differences Explained
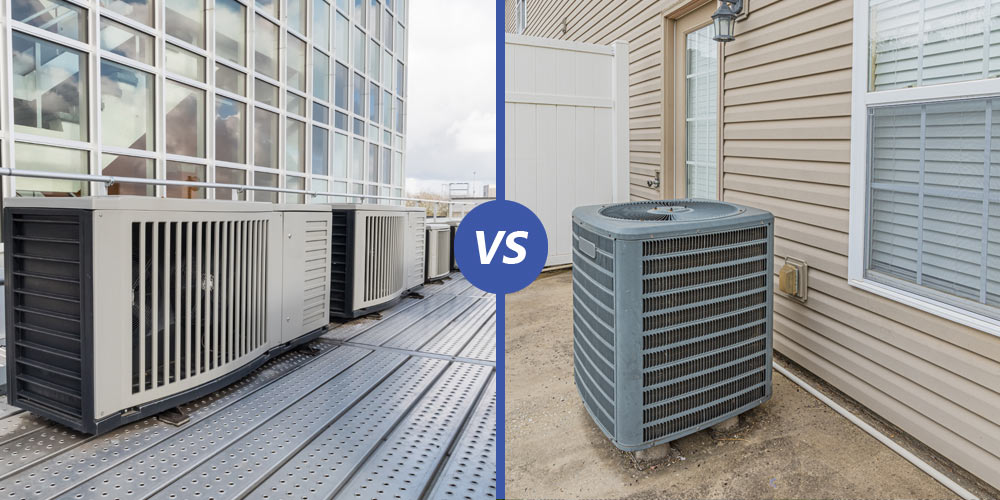

Are you curious about the differences between commercial and residential HVAC systems? Look no further! In this article, we will explore the key distinctions between these two types of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. Whether you’re a business owner or a homeowner, understanding these differences will help you make informed decisions when it comes to maintaining and managing the HVAC system in your space. So, let’s dive into the world of commercial and residential HVAC and uncover the factors that set them apart.
This image is property of acropolis-wp-content-uploads.s3.us-west-1.amazonaws.com.
Size and Scale
Commercial HVAC Systems
Commercial HVAC systems are designed to meet the cooling and heating demands of large-scale buildings such as offices, shopping malls, hospitals, and schools. These systems are robust and powerful, ensuring that they can handle the extensive square footage and complex layout of commercial spaces. The size and scale of commercial HVAC systems typically require multiple units to be installed in order to adequately distribute air throughout the building.
Residential HVAC Systems
On the other hand, residential HVAC systems are designed to meet the needs of individual houses, apartments, or small buildings. These systems are designed for smaller spaces and have a more compact size compared to commercial systems. Residential HVAC systems often consist of a single unit that can be located either outside or inside the building, such as in a basement or attic.
Complexity of Design
Commercial HVAC Systems
Due to the larger scale and complexity of commercial buildings, commercial HVAC systems are generally more intricate in design. These systems often include multiple components such as rooftop units, air handlers, chillers, boilers, and ductwork, all working together to provide efficient heating, cooling, and ventilation. The design of commercial HVAC systems requires careful consideration of factors like building layout, occupancy, and zoning requirements.
Residential HVAC Systems
Residential HVAC systems, on the other hand, are relatively simpler in design compared to their commercial counterparts. These systems typically consist of a furnace or heat pump, an air conditioner, and a network of ducts. The aim is to provide comfort to individual homes or small spaces, making the design less complex. However, residential systems can still vary in terms of size and efficiency, depending on the specific needs of the property.
Load Calculation
Commercial HVAC Systems
Load calculation is an essential step in designing commercial HVAC systems. It involves determining the amount of cooling or heating required to maintain a comfortable environment in the building, taking into account factors such as the size of the space, insulation, occupancy, and equipment load. Load calculations for commercial buildings tend to be more complex and detailed compared to residential load calculations due to the larger size and diverse usage of the spaces.
Residential HVAC Systems
Residential load calculation involves determining the cooling and heating needs of individual homes or small buildings. The calculation considers factors such as square footage, insulation levels, number of windows, and geographical location. While load calculations for residential HVAC systems may not be as intricate as those for commercial systems, they still play a crucial role in ensuring optimal comfort and energy efficiency.
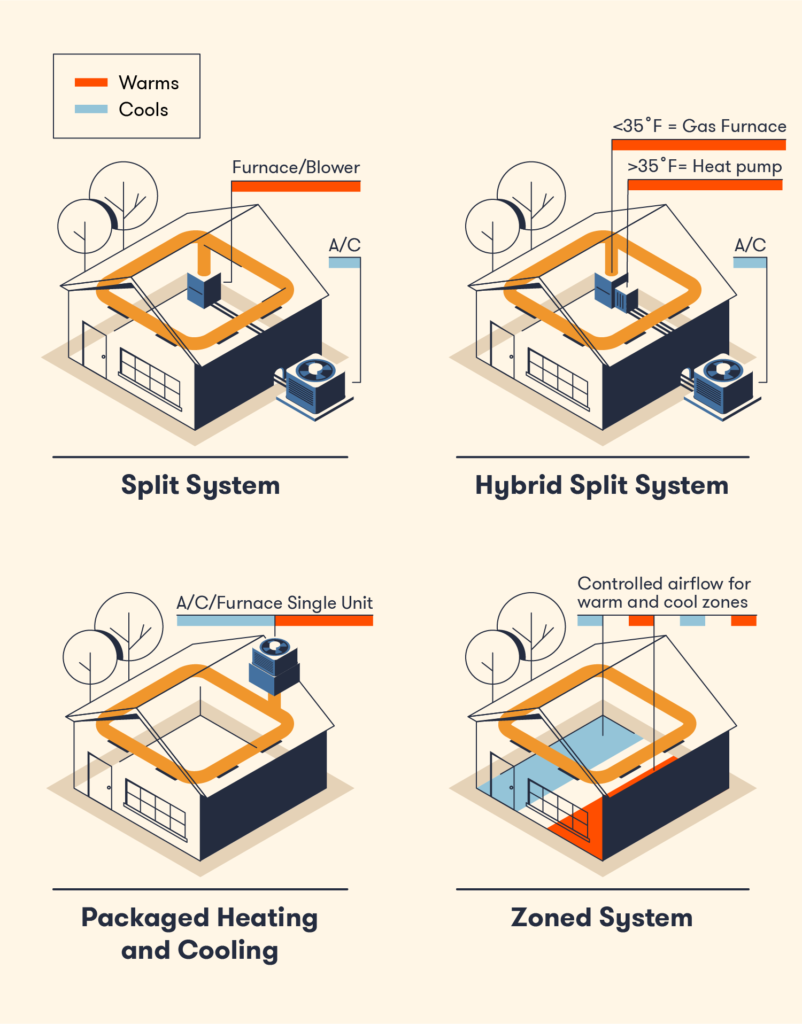
Zoning
Commercial HVAC Systems
Commercial HVAC systems often incorporate zoning to allow for different temperature settings in various areas of the building. Zoning enables individual control of each zone, accommodating diverse thermal requirements within the commercial space. This zoning flexibility is particularly useful in settings with varying occupancy levels or different temperature preferences, allowing for enhanced comfort and energy efficiency.
Residential HVAC Systems
Residential HVAC systems can also be equipped with zoning capabilities, although it is less common compared to commercial systems. Zoning in residential settings is typically achieved through the use of multiple thermostats and dampers within the ductwork. This allows for different temperature settings in different zones of the house, catering to individual preferences and increasing energy savings by only conditioning occupied areas.

This image is property of www.conejovalleyair.com.
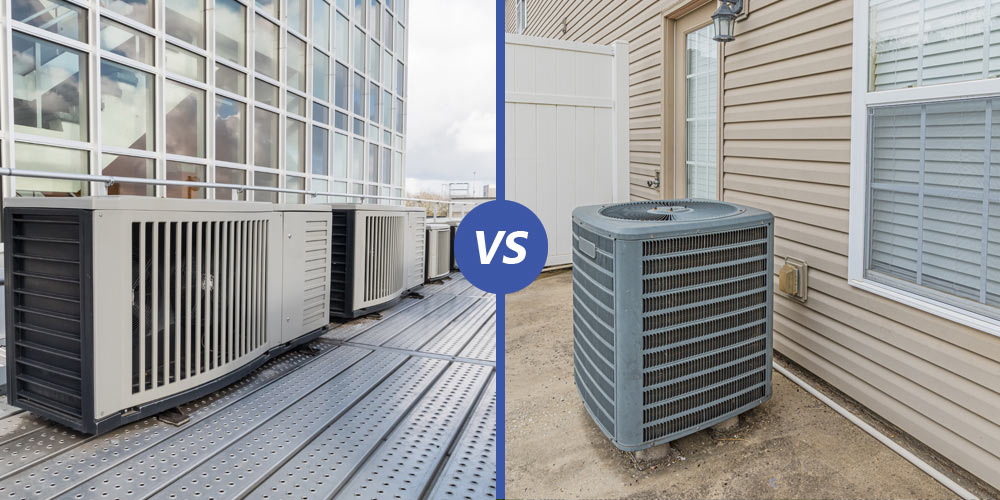
Ventilation
Commercial HVAC Systems
Proper ventilation is crucial in commercial buildings due to the higher occupancy levels and variety of activities taking place. Commercial HVAC systems incorporate ventilation components to maintain a constant supply of fresh air while efficiently removing stale air. These systems often include advanced ventilation features such as energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) and demand control ventilation (DCV) systems, ensuring a healthy and comfortable indoor environment.
Residential HVAC Systems
While ventilation is equally important in residential settings, the requirements are generally less complex compared to commercial buildings. Residential HVAC systems typically include ventilation components such as exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms, which help remove odors and excess moisture. However, innovative residential HVAC systems can also incorporate energy-efficient ventilation options like heat recovery ventilation (HRV) systems to maintain indoor air quality.
Energy Consumption
Commercial HVAC Systems
Commercial HVAC systems are designed to handle the high cooling and heating demands of large spaces, resulting in higher energy consumption compared to residential systems. The size, complexity, and continuous operation of commercial systems contribute to their higher energy usage. However, advancements in technology and the implementation of energy-efficient components have enabled significant energy savings in commercial HVAC systems.
Residential HVAC Systems
Residential HVAC systems typically consume less energy compared to commercial systems, mainly due to the smaller scale and intermittent operation. When properly maintained and paired with energy-efficient equipment, residential systems can achieve lower energy consumption while still providing the desired level of comfort. Energy-saving features such as programmable thermostats and high-efficiency equipment further contribute to reducing energy usage in residential HVAC systems.
This image is property of www.irishheatandair.com.
Maintenance and Repairs
Commercial HVAC Systems
Maintaining and repairing commercial HVAC systems requires specialized expertise due to the complexity of the equipment and the larger scale of the systems. Regular maintenance checks, including filter replacements, cleaning of coils, and inspection of ductwork, are essential to ensure optimum performance and prevent costly breakdowns. Commercial HVAC systems often require professional technicians with experience in handling the intricacies of these systems.
Residential HVAC Systems
Maintenance and repairs for residential HVAC systems are comparatively simpler and can often be performed by homeowners themselves. Routine tasks such as cleaning or replacing filters and checking for any visible damage can help keep the system in good working condition. However, professional maintenance is still recommended on an annual basis to ensure optimal efficiency and address any potential issues before they escalate.
Noise Level
Commercial HVAC Systems
Commercial HVAC systems, particularly those located on rooftops or in mechanical rooms, can generate considerable noise levels. The size, power, and multiple components of these systems contribute to the noise output. While noise reduction measures can be implemented, such as sound-insulating barriers or the use of quieter equipment, it is important to consider the noise impact on the building occupants, neighboring spaces, and local noise regulations.
Residential HVAC Systems
Residential HVAC systems are generally designed to operate with minimal noise to maintain the peace and comfort within the home. Although noise levels may vary depending on the specific equipment and installation, most residential systems employ noise-reducing technology to minimize any nuisance caused by the HVAC system. Routine maintenance and prompt repairs can also help identify and resolve any noise-related issues.
This image is property of acropolis-wp-content-uploads.s3.us-west-1.amazonaws.com.
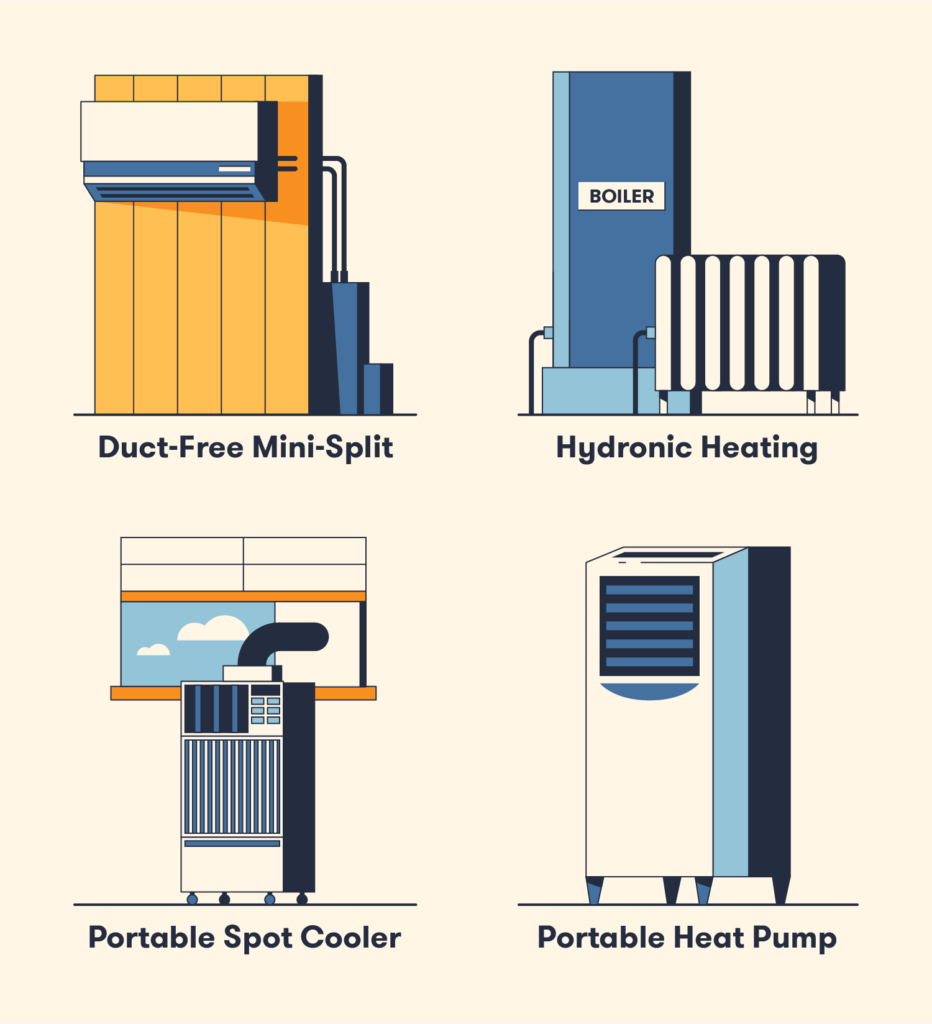
Cost
Commercial HVAC Systems
Commercial HVAC systems incur higher costs due to their larger scale, complexity, and customization requirements. The installation costs for commercial systems may include expenses such as equipment purchase, ductwork installation, and labor costs for system integration. Additionally, the operational and maintenance costs of commercial systems tend to be higher compared to residential systems, reflecting the increased energy consumption and ongoing professional maintenance.
Residential HVAC Systems
Residential HVAC systems generally have lower upfront costs compared to commercial systems. The equipment and installation expenses for a residential system are generally more affordable, especially for smaller spaces. Moreover, residential systems typically have lower operational costs, thanks to advances in energy-efficient technology and the smaller scale of the systems. Regular maintenance and efficient usage can further contribute to cost savings in residential HVAC systems.
Choosing the Right HVAC System
Factors to Consider for Commercial HVAC Systems
When selecting a commercial HVAC system, several factors need to be taken into consideration. The size and scale of the building, occupancy levels, intended usage, and zoning requirements all play a vital role. It is important to consult with HVAC professionals who can perform accurate load calculations, consider the specific needs of the commercial space, and recommend the most suitable and efficient system for the building.
Factors to Consider for Residential HVAC Systems
When choosing a residential HVAC system, factors such as the size of the living space, climate conditions, and energy efficiency should be considered. It is crucial to evaluate the heating and cooling needs of the home and select a system that matches those requirements. Additionally, homeowners should consider their budget, noise tolerance, and the availability of professional maintenance and repair services when choosing a residential HVAC system.
In conclusion, commercial and residential HVAC systems have distinct differences in terms of size, complexity, operational requirements, and cost. Commercial systems are designed to handle the cooling and heating demands of large-scale buildings, while residential systems cater to individual homes or small spaces. Both types of systems require careful consideration of various factors, including load calculation, zoning, ventilation, energy consumption, maintenance, and system selection. By Understanding these differences and considering the specific needs of the building or home, individuals can make informed decisions when it comes to HVAC system installation and maintenance.