HVAC Services
Get Professional Repairs From The Area's Trusted HVAC Technicians. Ask About Our Services! We Offer Professional Heating & Cooling System Repairs And Guarantee Long-Lasting Results.
Got Question? Call us: (850) 678-2665Financing
Understanding HVAC: The Basics For Homeowners
Discover the basics of HVAC systems for homeowners. From maintenance to system types, understand how to optimize your home's comfort and air quality.
Are you a homeowner trying to navigate the world of HVAC systems? Look no further! In this article, we’ll break down the basics of HVAC, providing you with all the information you need to understand and make informed decisions about your home’s heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. From the importance of regular maintenance to the different types of systems available, we’ll empower you to take control of your home’s comfort. So, grab a cup of coffee, sit back, and let’s delve into the world of HVAC together!
This image is property of redcapairconditioning.com.
What is HVAC?
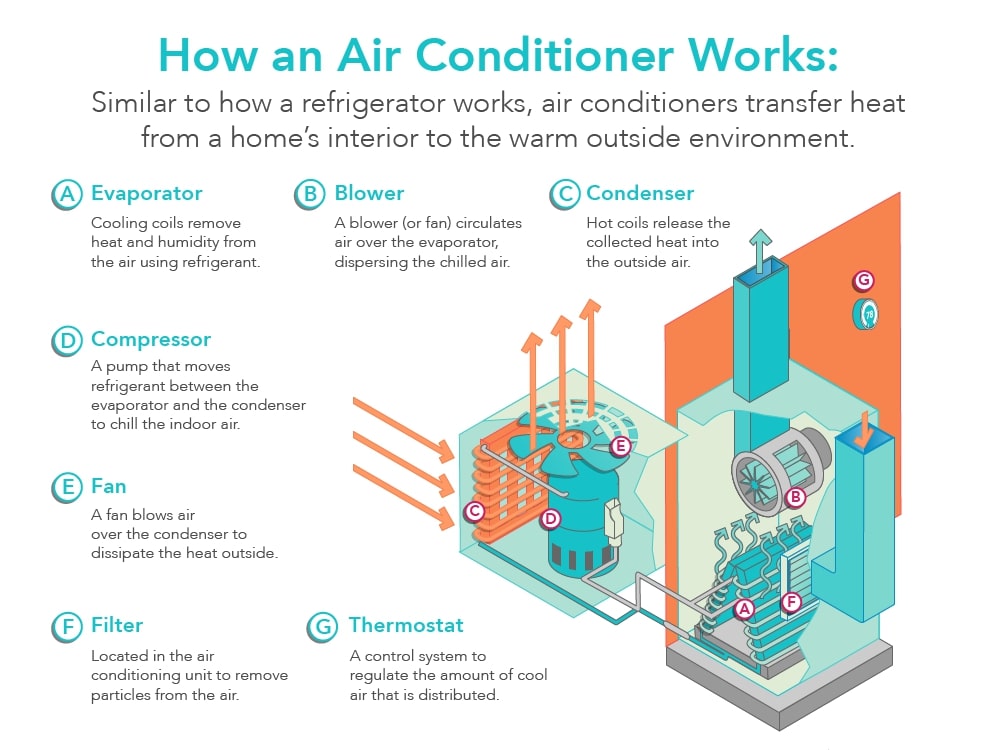
HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. It refers to the system used to regulate the temperature, humidity, and air quality in a building. Whether it’s your home, office, or any other indoor space, HVAC systems play a crucial role in providing comfort and maintaining a healthy environment.
Definition of HVAC
HVAC is a term used to describe the technology and systems that control the indoor climate of a building. It encompasses heating, cooling, and ventilation. HVAC systems work together to ensure that the temperature is regulated, the air is circulated and filtered, and the humidity levels are maintained within a comfortable range.
Components of HVAC system
HVAC systems consist of various components that work in harmony to provide heating, cooling, and ventilation. These include:
-
Heating and Cooling Units: These are the core components responsible for generating warm or cool air, such as furnaces, heat pumps, and air conditioners.
-
Ductwork: Ducts are used to distribute the conditioned air throughout the building. They carry the air from the heating or cooling unit to the different rooms or spaces.
-
Thermostats: Thermostats control the temperature by sensing the current climate and signaling the HVAC system to adjust accordingly. They allow you to set the desired temperature and customize the comfort level.
-
Vents and Registers: Vents and registers are openings in the walls, ceilings, or floors that allow the conditioned air to enter the living spaces and return the stale air back to the HVAC system.
-
Air Filters: HVAC systems use air filters to remove dust, allergens, and other particles from the air. These filters are essential for maintaining good indoor air quality.
-
Exhaust Fans: Exhaust fans remove stale air, moisture, and odors from spaces like bathrooms and kitchens. They play a crucial role in maintaining proper ventilation.
-
Dampers: Dampers are adjustable valves that control the airflow in the ductwork. They help regulate the amount of air entering specific areas of the building.
Heating
Types of heating systems
There are various types of heating systems commonly used in residential and commercial buildings. These include:
-
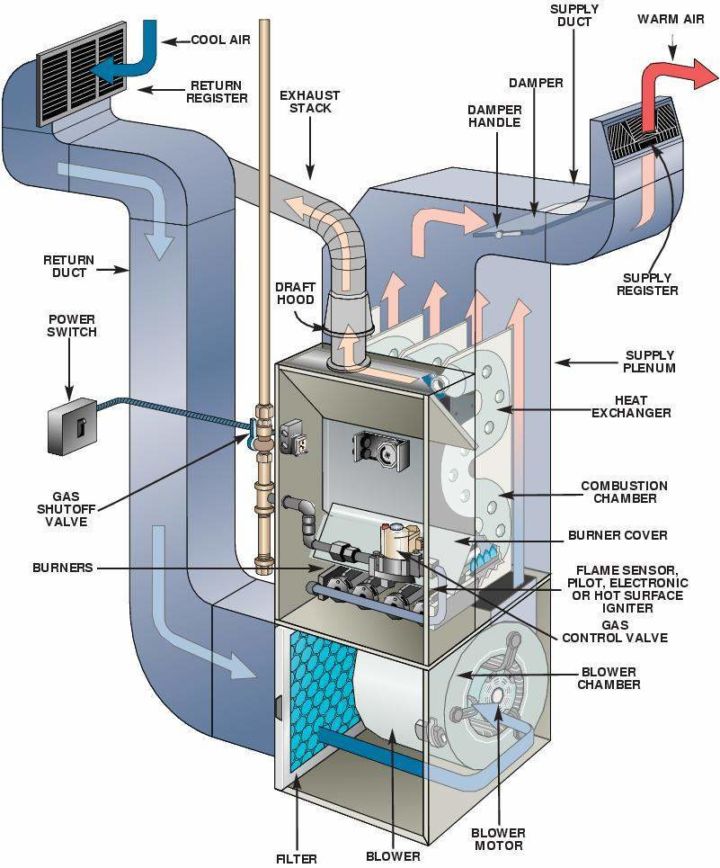
Furnaces: Furnaces are the most common type of heating system. They use fuel combustion or electric resistance to produce warm air, which is then circulated throughout the building via ductwork.
-
Heat Pumps: Heat pumps are versatile systems that can provide both heating and cooling. They extract heat from the air, ground, or water, and transfer it into the building during winter.
-
Boilers: Boilers heat water, which is then circulated through radiators or underfloor heating systems to warm up the space. They can be fueled by gas, oil, or electricity.
How heating systems work
Heating systems work by generating heat and distributing it throughout the building. Here’s a basic overview of how different types of heating systems operate:
-
Furnaces: Furnaces use either natural gas, oil, or electricity to create heat. This heat is then transferred to the air through a heat exchanger. The warm air is blown through the ductwork by a fan and delivered to the rooms via vents and registers.
-
Heat Pumps: Heat pumps work by extracting heat from the outdoor air, ground, or water source using a refrigerant. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the source and then transfers it indoors, where it is released into the air or used to warm up water.
-
Boilers: Boilers heat water, which is then circulated through a system of pipes to radiators, baseboard heaters, or underfloor heating systems. The hot water radiates heat, warming up the surrounding air.
Common heating issues
Heating systems can encounter various issues that may affect their overall performance. Some common heating problems include:
-
Insufficient Heating: If your heating system is not providing enough warmth, it could be due to a faulty thermostat, clogged air filters, or an issue with the heating unit itself.
-
Noisy Operation: Unusual noises coming from your heating system, such as rattling or banging, may indicate problems such as loose parts, motor issues, or airflow restrictions.
-
Uneven Heating: If certain areas of your building are significantly colder than others, it could be a result of ductwork blockages, leaks, or improper heat distribution from the heating unit.
Heating system maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the efficiency and longevity of your heating system. Here are some maintenance tasks you can perform:
-
Clean or Replace Air Filters: Dirty air filters can restrict airflow and reduce heating efficiency. Clean or replace them regularly to maintain good airflow and prevent dust and allergens from circulating in the indoor air.
-
Check Thermostat Settings: Ensure your thermostat is set correctly and functioning properly. Replace batteries if necessary and consider upgrading to a programmable thermostat for better temperature control and energy savings.
-
Clear Vents and Registers: Make sure all vents and registers are clear from dust, debris, or furniture obstructions. Blocked vents can prevent proper airflow, leading to increased strain on the heating system.
-
Schedule Professional Tune-Ups: It’s advisable to have a professional HVAC technician inspect and tune-up your heating system annually. They will clean the components, check for any issues, and optimize its performance.
Cooling
Types of cooling systems
Cooling systems are designed to remove heat from a building and maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. Here are the common types of cooling systems:
-
Air Conditioners: Air conditioning systems, also known as AC units, use refrigerants to absorb heat from indoor air and release it outside. They cool the air and reduce humidity, providing a refreshing indoor environment.
-
Heat Pumps: As mentioned earlier, heat pumps are versatile systems that can both heat and cool. In warm weather, heat pumps extract heat from indoor air and release it outside, effectively cooling the space.
-
Evaporative Coolers: Evaporative coolers, also known as swamp coolers, use water evaporation to cool the air. They work best in dry climates and are a cost-effective and energy-efficient cooling solution.
How cooling systems work
Cooling systems employ various mechanisms to lower the temperature and remove excess heat from the indoor environment. Let’s look at how different cooling systems work:
-
Air Conditioners: Air conditioners use a refrigeration cycle to cool indoor air. The system compresses and circulates refrigerant, which absorbs heat from the indoor air, and then releases it outside. The cooled air is blown back into the building through ductwork.
-
Heat Pumps: During the cooling mode, heat pumps reverse their operation compared to heating. Instead of extracting heat from the outdoor air or ground, they remove heat from the indoor air and release it outside, cooling the space.
-
Evaporative Coolers: Evaporative coolers use the natural process of evaporation to cool the air. Water is sprayed over pads, and a fan draws warm air through the damp pads, cooling it by evaporation. The cooled air is then circulated into the building.
Common cooling issues
Cooling systems can encounter certain issues that may affect their performance. Some common cooling problems include:
-
Insufficient Cooling: If your cooling system is not providing the desired cooling effect, it could be due to refrigerant leaks, dirty coils, or improper airflow caused by clogged filters or ductwork.
-
High Humidity: Excessive humidity in the indoor environment can make the space feel sticky and uncomfortable. Cooling systems, particularly air conditioners, are designed to remove humidity along with heat. If they are not functioning properly, high humidity can be an issue.
-
Strange Odors: Unpleasant odors emanating from the cooling system may be a sign of mold or bacterial growth, which can impact indoor air quality. It’s essential to address such issues promptly.
Cooling system maintenance
To ensure optimal performance and efficiency of your cooling system, regular maintenance is necessary. Here are some maintenance tasks to consider:
-
Clean or Replace Air Filters: Dirty filters restrict airflow and reduce cooling efficiency. Clean or replace the air filters regularly to maintain proper airflow and ensure the removal of dust and allergens from the air.
-
Check and Clean Condenser Coils: Outdoor condenser coils can accumulate dirt, debris, and vegetation. Regularly clean the coils to ensure unrestricted airflow and efficient heat transfer.
-
Clear Obstructions: Check for any obstructions around the outdoor unit, such as leaves, branches, or debris. These can restrict airflow and hinder the cooling process. Clear them regularly.
-
Schedule Professional Maintenance: It’s advisable to have a professional technician inspect and service your cooling system annually. They will check refrigerant levels, clean components, and ensure optimal performance.
Ventilation
Importance of ventilation
Ventilation plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy and comfortable indoor environment. It involves the exchange of indoor and outdoor air to remove pollutants, control moisture levels, and provide fresh air for breathing. Proper ventilation is essential for several reasons:
-
Air Quality: Ventilation helps remove pollutants and contaminants from indoor air, such as carbon dioxide, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and odors, improving the overall air quality.
-
Moisture Control: Ventilation helps control humidity levels, preventing excessive moisture buildup that can lead to mold growth, musty odors, and damage to building materials.
-
Temperature Regulation: Proper ventilation allows for effective temperature control. It helps remove excess heat during the summer and circulate warm air during the winter, maintaining a comfortable indoor climate.
Types of ventilation systems
There are different types of ventilation systems commonly used in residential and commercial buildings. Here are a few examples:
-
Natural Ventilation: Natural ventilation relies on the natural movement of air through windows, doors, and other openings. It takes advantage of breezes, temperature differences, and pressure variations to provide airflow.
-
Mechanical Ventilation: Mechanical ventilation involves the use of fans or blowers to circulate air and control airflow in a building. It can either be exhaust ventilation, supply ventilation, or balanced ventilation.
-
Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV) and Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV): HRV and ERV systems recover heat or energy from the outgoing air and transfer it to the incoming fresh air. They help reduce energy losses and maintain a consistent indoor temperature.
How ventilation systems work
Ventilation systems work by extracting stale indoor air and introducing fresh outdoor air into the building. Here’s a glimpse into the functioning of certain ventilation systems:
-
Natural Ventilation: Natural ventilation relies on the difference in air pressure and temperature to allow for air movement. Opening windows, doors, or vents enables the circulation of fresh air and the removal of stale air.
-
Mechanical Ventilation: Mechanical ventilation uses fans or blowers to force air movement. Exhaust ventilation systems extract air from specific areas, such as bathrooms or kitchens, while supply ventilation systems bring in fresh outdoor air. Balanced ventilation systems both extract and supply air, ensuring balanced airflow throughout the building.
-
HRV and ERV Systems: HRV and ERV systems use heat exchangers to transfer heat or energy between the outgoing and incoming air. This helps recover a significant portion of the energy that would otherwise be lost during ventilation.
Common ventilation issues
Ventilation systems can encounter various issues that may affect their performance. Some common ventilation problems include:
-
Inadequate Ventilation: Inadequate ventilation can result in poor indoor air quality, high humidity levels, and discomfort. It may be caused by undersized or blocked vents, malfunctioning fans, or outdated ventilation systems.
-
Condensation and Mold Growth: Insufficient ventilation can lead to excess moisture buildup, resulting in condensation on windows, walls, or ceilings. This moisture can create an ideal environment for mold and mildew growth.
-
Odors and Stale Air: Without adequate ventilation, odors from cooking, pets, or other sources can linger, making the indoor environment unpleasant. Stale air can also contribute to a stuffy and uncomfortable atmosphere.
Ventilation system maintenance
Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of your ventilation system. Here are some maintenance tasks you can perform:
-
Clean and Unblock Vents: Regularly inspect and clean the vents and registers in your building. Remove any obstructions, dust, or debris that can hinder airflow and affect ventilation.
-
Test and Clean Exhaust Fans: Exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens play a vital role in removing moisture and odors. Test and clean these fans regularly to ensure optimal performance.
-
Check and Replace Filters: If your ventilation system uses filters, such as in HRV or ERV systems, check and replace them as recommended by the manufacturer. Dirty filters can hinder airflow and reduce efficiency.
-
Schedule Professional Inspection: It’s advisable to have a professional HVAC technician inspect your ventilation system as part of regular HVAC maintenance. They can identify any issues, clean components, and optimize ventilation performance.
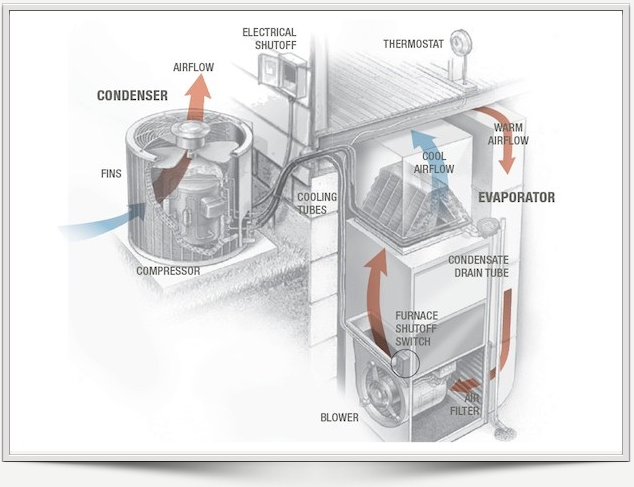
This image is property of simpleaircare.com.
Air Quality
The significance of Indoor Air Quality (IAQ)
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) refers to the condition of the air inside a building and its potential impact on the health and comfort of its occupants. Good IAQ is essential for maintaining a healthy living or working environment. Poor IAQ can lead to various health issues, such as allergies, respiratory problems, and discomfort.
Factors affecting IAQ
Several factors can affect indoor air quality. Understanding these factors is crucial for identifying potential sources of contaminants and improving IAQ. Here are some common factors:
-
Pollutants: Indoor air can contain various pollutants, such as dust, pollen, pet dander, VOCs, mold spores, and bacteria. These pollutants can originate from sources like building materials, furniture, cleaning products, and outdoor pollutants entering the building.
-
Ventilation: Inadequate ventilation hampers the exchange of fresh outdoor air, resulting in stagnation and pollutant buildup indoors. Insufficient ventilation can lead to poor IAQ and increased levels of indoor pollutants.
-
Humidity Levels: High humidity can promote mold growth and the proliferation of dust mites, while low humidity can cause dryness and discomfort. Proper humidity control is essential for maintaining good IAQ.
How HVAC systems contribute to IAQ
HVAC systems play a crucial role in maintaining good IAQ. They contribute to IAQ in the following ways:
-
Filtration: HVAC systems use air filters to trap dust, pollen, pet dander, and other airborne particles. Filters help improve IAQ by removing these pollutants from the circulated air.
-
Ventilation: HVAC systems provide ventilation, exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air. Proper ventilation ensures the removal of indoor pollutants and the introduction of clean air.
-
Humidity Control: Some HVAC systems incorporate humidifiers and dehumidifiers to regulate indoor humidity levels. By controlling moisture, HVAC systems inhibit mold growth and maintain a comfortable and healthy indoor environment.
Maintaining good IAQ
Maintaining good IAQ is crucial for the health and well-being of building occupants. Here are some steps you can take to improve and maintain good IAQ:
-
Regularly Clean and Dust: Regular cleaning and dusting of surfaces, floors, and furniture help remove dust, allergens, and other pollutants from the indoor environment.
-
Keep Humidity in Check: Monitor indoor humidity levels and use humidifiers or dehumidifiers to maintain optimal humidity. Aim for a relative humidity of around 40-60% for optimal comfort and to prevent mold growth.
-
Proper Ventilation: Ensure that your HVAC system provides adequate ventilation. Regularly open windows and doors to introduce fresh outdoor air, particularly in well-ventilated areas or when the weather permits.
-
Use High-Quality Air Filters: Invest in high-quality air filters that can effectively capture smaller particles and allergens. Regularly clean or replace these filters as recommended by the manufacturer to ensure optimal filtration efficiency.
Energy Efficiency
The importance of energy efficiency in HVAC systems
Energy efficiency is a crucial aspect of HVAC systems, as it not only saves you money on utility bills but also helps reduce your carbon footprint. Efficient HVAC systems consume less energy, leading to lower energy bills and environmental impact.
Tips for increasing energy efficiency
Here are some tips to help increase energy efficiency and optimize the performance of your HVAC system:
-
Proper Insulation: Ensure that your building is properly insulated, as this helps prevent heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. Poor insulation can put unnecessary strain on your HVAC system and lead to energy inefficiency.
-
Regular Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance for your HVAC system to ensure that it operates at its peak efficiency. Professional inspections, cleaning, and tune-ups can identify and address any issues that may affect energy efficiency.
-
Air Filter Maintenance: Clean or replace your HVAC system’s air filters regularly. Clogged filters restrict airflow, forcing the system to work harder and consume more energy.
-
Smart Thermostats: Consider upgrading to a programmable or smart thermostat. These thermostats allow you to set temperature schedules based on your occupancy patterns, optimizing energy usage and reducing wastage.
-
Zoning Systems: If possible, implement zoning systems, which allow you to control the temperature in different areas of your building independently. This helps avoid heating or cooling unoccupied spaces, saving energy.
Programmable thermostats and their benefits
Programmable thermostats offer several benefits in terms of energy efficiency and convenience. Here are some advantages:
-
Energy Savings: Programmable thermostats allow you to set different temperature schedules for different times of the day. You can adjust the temperature automatically to reduce heating or cooling when it’s not needed, resulting in energy savings.
-
Customized Comfort: With programmable thermostats, you have the flexibility to set the temperature to your desired comfort level, ensuring optimal comfort when you are at home and energy savings when you are away.
-
Convenience: Programmable thermostats eliminate the need for manual adjustments every time you leave or enter your premises. Once the schedule is set, the thermostat automatically maintains the desired temperature, providing convenience and peace of mind.
-
Remote Access: Many programmable thermostats offer remote access through smartphone apps. This allows you to adjust the temperature settings even when you are away from home, providing flexibility and control.
Energy-saving HVAC technologies
Technological advancements in the HVAC industry have led to the development of energy-saving HVAC technologies. These technologies help maximize energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Some examples include:
-
Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) Systems: VRF systems provide individualized control over each zone or room, optimizing energy usage by adjusting refrigerant flow based on demand.
-
Geothermal HVAC Systems: Geothermal systems use the constant temperature of the earth to heat and cool buildings. They are highly energy-efficient, as they harness renewable geothermal energy.
-
High-efficiency Heat Pumps: High-efficiency heat pumps can significantly reduce energy consumption by extracting heat from the outside air, ground, or water sources.
-
Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV) Systems: ERV systems recover both heat and moisture from the outgoing air and transfer it to the incoming fresh air, reducing energy losses and maintaining a pleasant indoor environment.
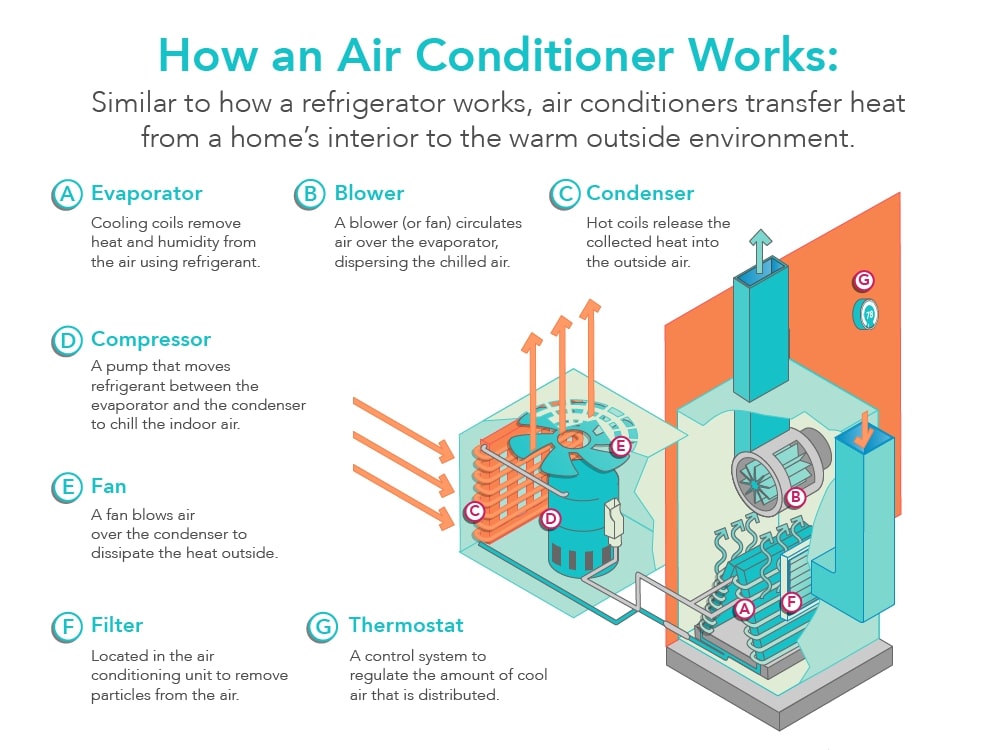
This image is property of jacobsheating.com.
System Sizing
Why proper HVAC system sizing is important
Proper HVAC system sizing is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency. An oversized or undersized system can lead to issues such as inefficient operation, discomfort, increased energy consumption, and frequent breakdowns.
How HVAC professionals determine the right size
HVAC professionals use Manual J calculations to determine the right size for an HVAC system. Manual J takes into account various factors such as the building’s square footage, insulation levels, orientation, window size and type, occupancy, and local climate conditions. This thorough calculation helps accurately determine the heating and cooling requirements of the building.
Consequences of improper system sizing
Improper system sizing can have several negative consequences. Here are some common problems associated with oversized or undersized HVAC systems:
-
Inefficiency: Oversized systems frequently short-cycle, turning on and off more frequently than necessary. This results in wasted energy and reduces the system’s efficiency.
-
Temperature Discrepancies: Improperly sized systems may struggle to distribute conditioned air evenly throughout the building, resulting in temperature discrepancies and discomfort.
-
Increased Operating Costs: Oversized systems consume more energy than necessary, leading to higher energy bills. Undersized systems may work harder and run for prolonged periods, also increasing energy consumption.
-
Reduced Lifespan: An improperly sized system may experience more wear and tear due to frequent cycling or excessive strain, leading to premature breakdowns and reduced lifespan.
-
Comfort Issues: Oversized systems may cool or heat the space too quickly, creating temperature swings and discomfort. Undersized systems may struggle to meet demand, resulting in inadequate heating or cooling.
Choosing and Installing HVAC Systems
Factors to consider when choosing HVAC systems
Choosing the right HVAC system for your building requires careful consideration of several factors. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
-
Building Size and Layout: Consider the square footage, number of rooms, and layout of your building to determine the heating and cooling requirements. This will help in selecting the appropriate system size and configuration.
-
Energy Efficiency: Look for HVAC systems with high energy efficiency ratings. Energy-efficient systems consume less energy, resulting in lower utility bills and reduced environmental impact.
-
Climate Conditions: Take your local climate conditions into account when selecting an HVAC system. Consider factors such as temperature extremes, humidity levels, and seasonal variations.
-
Noise Level: HVAC systems can produce noise during operation. Consider the noise levels of different systems and choose one that meets your comfort requirements, especially for residential settings.
Different types of HVAC systems
There are several types of HVAC systems available, each with its own advantages and suitable applications. Here are some common types:
-
Split System: Split systems consist of both indoor and outdoor units. They are commonly used in residential buildings and small commercial spaces. Split systems provide both heating and cooling.
-
Packaged System: Packaged systems contain all the components in a single unit, typically installed outside the building. They are suitable for buildings with limited indoor space and are available in various configurations for heating and cooling.
-
Ductless Mini-Split System: Ductless mini-split systems consist of an outdoor unit and one or more indoor units. They are a good option for buildings without ductwork or when zoning is desired for customized control.
-
Geothermal Heat Pump: Geothermal systems use the constant temperature of the earth to heat and cool buildings. They are highly energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Common installation mistakes to avoid
Installing an HVAC system requires careful attention to detail to avoid common mistakes that can impact its performance. Here are some installation mistakes to avoid:
-
Improper Sizing: Ensure that the HVAC system is properly sized according to Manual J calculations. Oversized or undersized systems can lead to inefficiency, discomfort, and increased wear and tear.
-
Incorrect Refrigerant Charge: Incorrect refrigerant charge can affect system performance and efficiency. It’s important to follow manufacturer guidelines and ensure proper refrigerant charge during installation.
-
Improper Ductwork Installation: Poorly designed or installed ductwork can lead to airflow issues, temperature inconsistencies, and energy loss. Ductwork should be installed correctly, sealed, and insulated to ensure optimal performance.
-
Inadequate Insulation: Insufficient insulation around ducts, pipes, and equipment can result in energy loss, condensation issues, and reduced efficiency. Proper insulation is crucial to prevent energy wastage.
Finding the right HVAC contractor
Finding the right HVAC contractor is essential to ensure a successful installation. Here are some key considerations when selecting an HVAC contractor:
-
Licensing and Certification: Verify that the contractor holds the necessary licenses and certifications required by local regulations. This ensures that they have the required knowledge and expertise.
-
Experience and Reputation: Look for HVAC contractors with sufficient experience and a good reputation within the community. Read customer reviews, ask for references, and check online ratings for insights into their performance.
-
Comprehensive Services: Consider contractors that offer a wide range of HVAC services, including installation, maintenance, and repairs. Choosing a contractor who can provide comprehensive support throughout the lifespan of your HVAC system can be beneficial.
-
Estimates and Guarantee: Request written estimates from multiple contractors, specifying the scope of work, costs, and timelines. Inquire about warranties and guarantees to ensure that you have recourse in case of any issues.
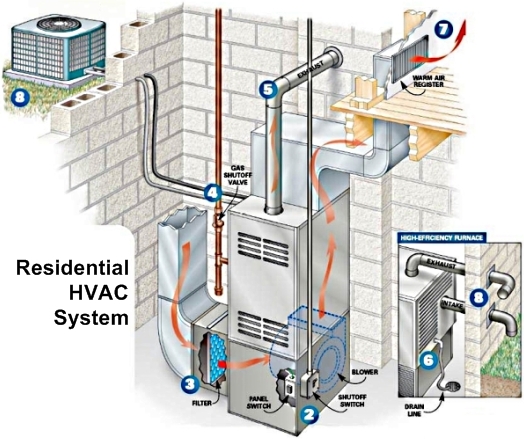
This image is property of besttipsfortraining.files.wordpress.com.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
The importance of regular HVAC maintenance
Regular HVAC maintenance is essential for the longevity and performance of your system. Here are the key reasons why maintenance is important:
-
System Efficiency: Regular maintenance helps keep your HVAC system running at peak efficiency. A well-maintained system operates more effectively, reducing energy consumption and utility costs.
-
Reliability: Proper maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate into costly breakdowns. Regular inspections and tune-ups can help prevent unexpected failures and ensure reliable operation.
-
Indoor Air Quality: HVAC maintenance includes cleaning and replacing filters, removing debris, and inspecting components that impact indoor air quality. Clean and well-maintained systems contribute to a healthier and more comfortable indoor environment.
DIY maintenance tips
While professional HVAC maintenance is recommended, there are some maintenance tasks that you can perform yourself to keep your system in good shape. Here are some DIY maintenance tips:
-
Regularly Clean or Replace Air Filters: Dirty filters restrict airflow and reduce system efficiency. Clean or replace filters as recommended by the manufacturer to maintain proper airflow and improve indoor air quality.
-
Keep Outdoor Units Free from Debris: Regularly inspect the outdoor unit and remove any debris, such as leaves, branches, or dirt. Blocked airflow can decrease efficiency and strain the system.
-
Check and Clear Condensate Drain: Locate the condensate drain line and check for any blockages. Clean the drain line or use a wet-dry vacuum to remove any clogs. A clogged condensate drain can cause water damage and affect system performance.
-
Clean Vents and Registers: Wipe down vents and registers regularly to remove dust and debris. Blocked vents can hinder airflow, causing strain on the system and reduced comfort.
Signs of HVAC problems
It’s important to be aware of the signs that indicate potential problems with your HVAC system. Prompt identification of issues can help prevent further damage and minimize repair costs. Here are some signs to look out for:
-
Inconsistent Temperatures: Uneven heating or cooling across different rooms or areas of your building may indicate airflow issues, faulty thermostats, or problems with the HVAC system.
-
Strange Noises: Unusual sounds such as grinding, buzzing, rattling, or banging can point to motor issues, loose components, or airflow problems. These sounds should be investigated promptly.
-
High Energy Bills: A sudden increase in energy bills without any significant change in usage may indicate that your HVAC system is not operating efficiently. It could be due to leaks, clogged filters, or other issues.
-
Frequent Cycling: HVAC systems should cycle on and off according to the temperature settings. If your system is frequently cycling or running continuously, it may indicate a problem that needs attention.
When to call a professional
While some HVAC maintenance tasks can be performed by homeowners, certain issues require professional intervention. It’s advisable to call a professional HVAC technician in the following situations:
-
Major Repairs: If your HVAC system requires significant repairs, it’s best to leave the job to a professional. They have the expertise, tools, and experience to diagnose and address complex issues.
-
Refrigerant Leaks: Handling refrigerants requires specialized training and equipment. If you suspect a refrigerant leak, it’s crucial to contact a professional technician who can safely address the issue.
-
Electrical Problems: HVAC systems involve electrical components. If you notice any electrical issues, such as tripped breakers or faulty wiring, it’s essential to contact a professional to ensure your safety.
-
Warranty and Maintenance Contracts: If your HVAC system is under warranty or covered by a maintenance agreement, it’s advisable to adhere to the specified terms. This often includes professional maintenance, which helps maintain warranty validity.
Costs and Financing
Factors affecting HVAC costs
Several factors can influence the costs associated with HVAC installation or repairs. Here are some common factors:
-
System Size and Configuration: The size and complexity of the HVAC system required for your building will impact the overall cost. Larger systems or systems with advanced features tend to be more expensive.
-
Efficiency Ratings: Higher efficiency ratings generally result in higher initial costs. However, energy-efficient systems offer long-term savings in the form of reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills.
-
Labor Costs: Labor costs vary based on factors such as the complexity of the installation, the duration of the project, and regional labor rates.
-
Ductwork: If your building requires new or extensive ductwork installation or modifications, it can add to the overall cost. Ductwork complexity, material selection, and access difficulty affect the cost.
Average costs of HVAC systems
The cost of installing or replacing an HVAC system can vary depending on various factors. Here are some rough estimates for HVAC system costs:
-
Central Air Conditioning: The average cost of installing a central air conditioning system can range from $2,500 to $7,500, depending on factors such as system size, efficiency, and installation complexity.
-
Furnace: The average cost of installing a furnace can range from $2,000 to $6,000, depending on factors such as fuel type, efficiency, and regional labor rates.
-
Heat Pump: The average cost of installing a heat pump system can range from $3,500 to $8,000, depending on factors such as size, efficiency, and installation complexity.
-
Ductless Mini-Split: The cost of installing a ductless mini-split system can range from $1,500 to $5,000 per indoor unit, depending on factors such as the number of units, capacity, and installation complexity.
Financing options for HVAC installation or repairs
Financing options can help make HVAC installation or repairs more affordable. Here are some common financing options available:
-
Manufacturer or Retailer Financing: HVAC manufacturers or retailers often offer financing plans with flexible payment options to help customers afford the cost of HVAC systems.
-
Home Improvement Loans: Home improvement loans are specifically designed for financing home improvement projects. These loans provide funds upfront, allowing homeowners to cover the cost of HVAC installation or repairs.
-
Energy-Efficiency Financing Programs: Many regions offer financing programs or incentives to encourage energy-efficient upgrades. These programs provide loans or grants to homeowners who opt for energy-efficient HVAC systems.
-
Personal Loans and Credit Cards: Personal loans or credit cards can be used to finance HVAC installation or repairs. However, it’s essential to consider the interest rates and terms associated with these options.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of HVAC is essential for homeowners to make informed decisions about heating, cooling, ventilation, and indoor air quality. By recognizing the importance of proper system sizing, maintenance, and energy efficiency, homeowners can ensure comfort, efficiency, and a healthy indoor environment. With proper knowledge, reliable professional assistance, and a focus on long-term sustainability, homeowners can optimize their HVAC systems for years of reliable service.