

HVAC Services
Get Professional Repairs From The Area's Trusted HVAC Technicians. Ask About Our Services! We Offer Professional Heating & Cooling System Repairs And Guarantee Long-Lasting Results.
Got Question? Call us: (850) 678-2665Financing
The Importance of Insulation in HVAC Efficiency
Maximize HVAC efficiency and reduce energy costs with proper insulation and sealing. Learn the benefits of insulation and sealing techniques in this informative post.
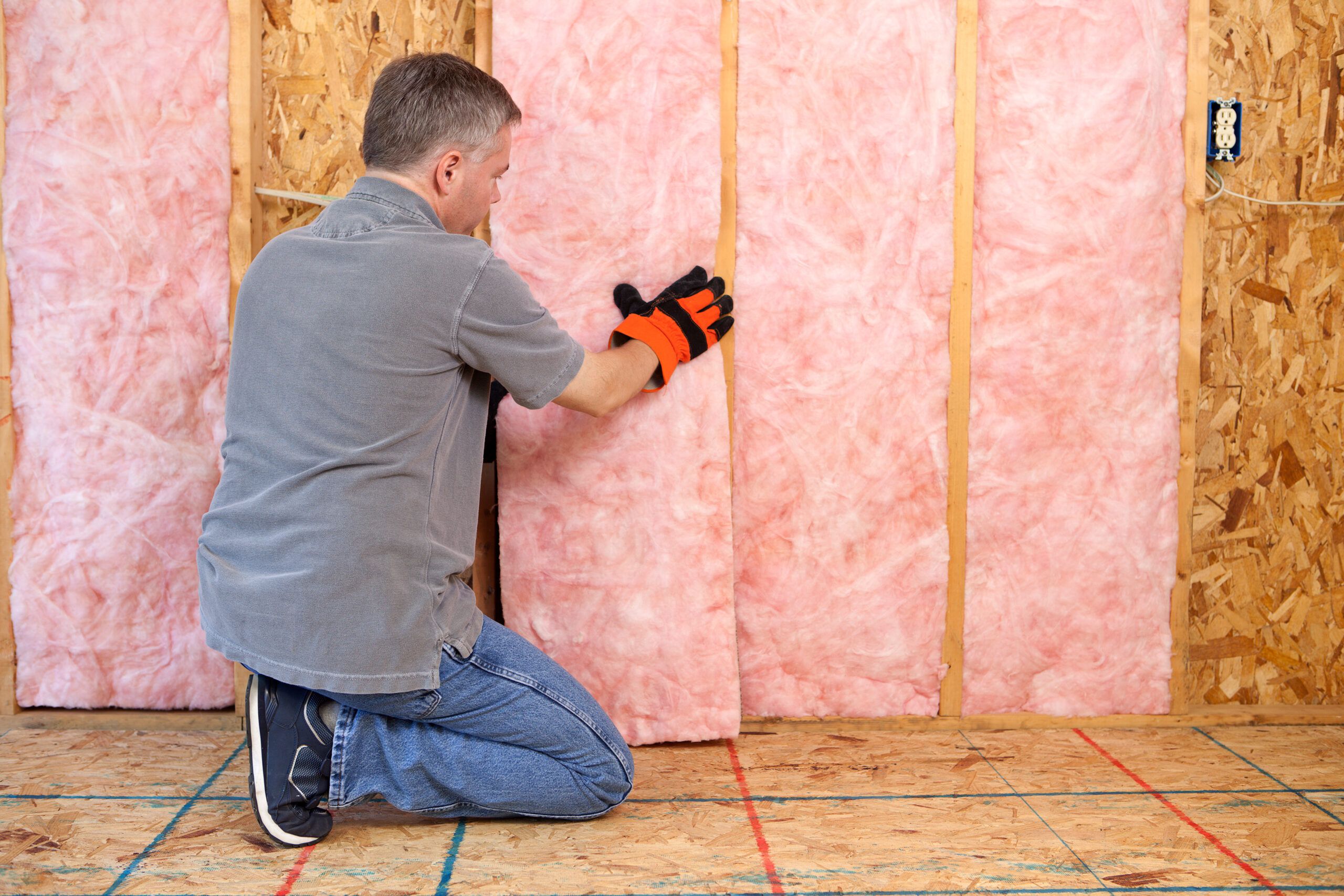

If you want to maximize the efficiency of your HVAC system and reduce energy costs, it’s crucial to pay attention to insulation and sealing. Insulation plays a significant role in maintaining a consistent temperature inside your home, preventing any heat loss or gain. It acts as a protective barrier, keeping the desired indoor temperature stable regardless of the weather conditions outside. Additionally, sealing any air leaks in your HVAC system ensures that conditioned air stays inside, enhancing its overall efficiency. By giving attention to insulation and sealing, you can create a comfortable living environment while optimizing energy consumption. Contact Tempacure Heating and Air Conditioning for expert HVAC service, repair, and maintenance in Niceville, FL, and the surrounding area.
The Importance of Insulation in HVAC Efficiency
When it comes to HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, insulation plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal efficiency. Proper insulation helps to reduce heat loss and gain, improve energy efficiency, enhance indoor comfort, increase equipment lifespan, lower energy bills, and minimize environmental impact. By understanding the importance of insulation in HVAC efficiency, you can make informed decisions to maximize the performance and longevity of your heating and cooling systems.
1.1 Reducing Heat Loss and Gain
Insulation acts as a barrier between the indoor and outdoor environments, reducing the transfer of heat between the two. In the winter, well-insulated spaces retain warmth and prevent cold air from infiltrating, thereby reducing the workload on your heating system. Similarly, in the summer, insulation keeps the cool air inside and prevents hot air from entering, reducing the strain on your cooling system. By minimizing heat loss and gain, insulation helps to maintain a consistent indoor temperature and decrease the demand for heating and cooling.
1.2 Improving Energy Efficiency
By reducing the need for excess heating and cooling, insulation directly contributes to improving energy efficiency in HVAC systems. When there is insufficient insulation, HVAC equipment has to work harder and consume more energy to achieve the desired indoor temperature. This results in higher energy bills and greater strain on the system. With proper insulation, you can achieve optimal energy efficiency, reducing your carbon footprint and saving money on utility bills.
1.3 Enhancing Indoor Comfort
Insufficient insulation can lead to temperature fluctuations, uncomfortable drafts, and cold spots in your home. In contrast, well-insulated spaces provide consistent and comfortable indoor temperatures, ensuring a pleasant environment for you and your family. Whether it’s keeping warm during the winter or staying cool in the summer, proper insulation helps to create a comfortable living space free from hot or cold extremes.
1.4 Increasing Equipment Lifespan
HVAC equipment, such as furnaces, air conditioners, and heat pumps, have a finite lifespan. However, poor insulation can accelerate wear and tear on these systems, leading to premature breakdowns and costly repairs. By reducing the workload on your HVAC equipment through effective insulation, you can extend their lifespan and minimize the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Investing in proper insulation can ultimately save you money in the long run by maximizing the durability and longevity of your HVAC equipment.
1.5 Lowering Energy Bills
One of the most tangible benefits of proper insulation in HVAC systems is the potential for significant energy savings. When your heating and cooling systems are not overworked due to inadequate insulation, they consume less energy, resulting in lower utility bills. Insulating your home effectively can help to create an energy-efficient building envelope, reducing heat transfer and minimizing the need for constant heating or cooling. This translates into substantial savings over time and increased financial flexibility for other priorities.
1.6 Minimizing Environmental Impact
An often overlooked aspect of insulation in HVAC efficiency is its role in reducing the environmental impact associated with energy consumption. By improving energy efficiency, insulation helps to lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduce reliance on fossil fuel-powered electricity generation. By minimizing the demand for heating and cooling energy, effective insulation contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to residential and commercial building operations.
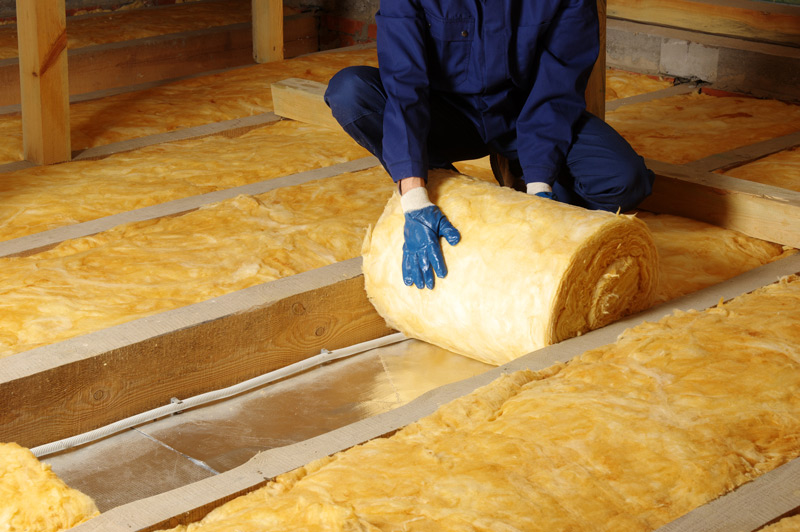

This image is property of ardmorefreshair.com.
2. Insulation Types for HVAC Systems
To achieve the desired benefits of insulation in HVAC systems, it is essential to choose the right type of insulation for your specific needs. Here are some common insulation types used in HVAC applications:
2.1 Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation is one of the most common and widely used insulation materials. It consists of glass fibers that are loosely spun together, creating a fluffy and lightweight material. Fiberglass insulation is known for its excellent thermal performance, sound absorption qualities, and fire resistance. It is relatively affordable and easy to install, making it a popular choice for various HVAC applications.
2.2 Cellulose Insulation
Cellulose insulation is made from recycled paper products, primarily newspaper. It is treated with fire-retardant chemicals to enhance its safety features. Cellulose insulation offers excellent thermal resistance, soundproofing qualities, and resistance to air infiltration. It is particularly effective in retrofitting existing structures and filling cavities that may be difficult to access with other types of insulation.
2.3 Spray Foam Insulation
Spray foam insulation is a versatile and highly effective insulation option. It is applied as a liquid that expands and hardens into a solid foam, creating an airtight barrier. Spray foam insulation provides superior thermal resistance, air sealing properties, moisture control, and sound absorption capabilities. It can be applied in various areas, including attics, walls, and around air ducts, offering excellent coverage and insulation performance.
2.4 Radiant Barrier Insulation
Radiant barrier insulation is specifically designed to reflect heat rather than absorb it. It consists of a reflective surface, often made of aluminum foil, which is installed in attics and on the underside of roofs. Radiant barrier insulation helps to reduce radiant heat transfer, keeping your home cooler in hot climates and preventing heat loss in colder climates. It works by reflecting the sun’s radiant energy away from the building, reducing the need for excessive cooling.
2.5 Vapor Barrier Insulation
Vapor barrier insulation is designed to prevent moisture from entering the building envelope. It consists of materials with low moisture permeability, such as plastic or foil. Vapor barrier insulation is typically installed on the warm side of the insulation, ensuring that warm, moist air does not reach the cooler surfaces where condensation can occur. By controlling moisture infiltration, vapor barrier insulation helps to prevent mold growth, rotting, and other moisture-related issues.
2.6 Reflective Insulation
Reflective insulation utilizes reflective materials, such as foil, to reduce radiant heat transfer. It is commonly used in HVAC applications to enhance energy efficiency by reflecting radiant energy back into the space. Reflective insulation can be installed in attics, crawlspaces, and on the underside of roofs to reduce heat gain in the summer and heat loss in the winter. It complements other forms of insulation by providing an additional layer of thermal protection.
2.7 Duct Insulation
Duct insulation focuses on insulating the ductwork, which is responsible for distributing conditioned air throughout your home or building. Insulating the ducts helps to minimize heat loss or gain during the distribution process, ensuring that the air reaches its intended destination at the desired temperature. By preventing energy losses in the ductwork, duct insulation improves overall HVAC system efficiency and reduces energy waste.
2.8 Attic Insulation
Attic insulation plays a crucial role in preventing heat loss and gain through the roof. Since heat naturally rises, an uninsulated or poorly insulated attic can lead to significant energy losses. Proper attic insulation, such as blown-in insulation or batt insulation, helps to create a thermal barrier, reducing the transfer of heat between the attic and the conditioned spaces below.
2.9 Wall Insulation
Wall insulation is essential for maintaining a consistent indoor temperature and reducing thermal bridging. Depending on the construction of your walls, various insulation options may be applicable, such as cavity wall insulation, blown-in insulation, or rigid foam insulation. Insulating the walls helps to prevent heat flow through the building envelope, improving energy efficiency and enhancing occupant comfort.
2.10 Floor Insulation
Floor insulation is crucial for homes with unheated spaces below, such as crawlspaces or garages. Insulating the floor above the unheated spaces helps to minimize heat loss, reduce drafts, and improve overall comfort. By separating the conditioned space from the unheated areas, floor insulation prevents cold air from infiltrating the living space and lowers the demand for heating.
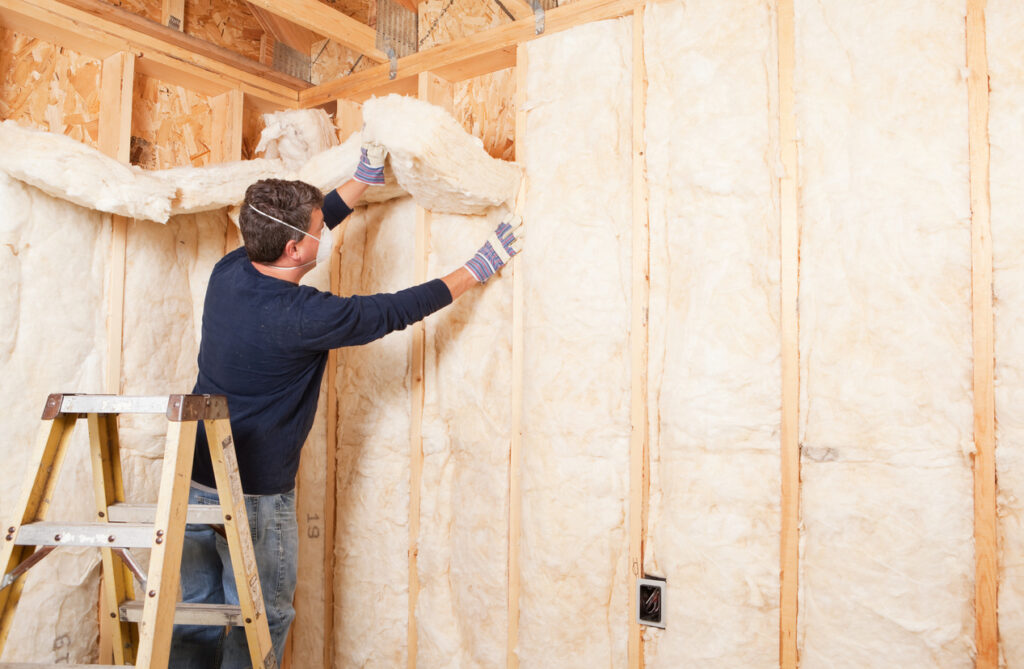

This image is property of blog.hartmanbrothers.com.
3. Sealing Techniques for HVAC Efficiency
In addition to insulation, proper sealing is essential for optimizing HVAC efficiency. Air leaks, gaps, and cracks in the building envelope can significantly impact the performance of your heating and cooling systems. Here are some sealing techniques to consider:
3.1 Duct Sealing
Duct sealing involves identifying and sealing any leaks or gaps in the ductwork. Leaky ducts can lead to significant energy losses, as conditioned air escapes into unconditioned spaces. By sealing the ducts, you can maximize the delivery of conditioned air to the intended areas, reducing energy waste and improving comfort.
3.2 Air Sealing
Air sealing focuses on sealing air leaks in the building envelope, such as gaps around windows and doors, cracks in walls, and openings around utility penetrations. By reducing air infiltration, air sealing helps to maintain the desired indoor temperature, prevent drafts, and improve energy efficiency. Common air sealing techniques include using weatherstripping, caulking, and expanding foam.
3.3 Weatherstripping
Weatherstripping involves sealing gaps around windows and doors to prevent air leakage. Weatherstripping materials, such as adhesive-backed foam tape or V-strip, are applied to the edges of windows and doors to create a tight seal when closed. Proper weatherstripping helps to eliminate drafts, reduce energy loss, and maintain a comfortable indoor environment.
3.4 Caulking
Caulking is used to seal small gaps and cracks in walls, ceilings, and other building components. It is commonly applied around windows, doors, and baseboards to prevent air infiltration. Caulk comes in various formulations, such as silicone, latex, or acrylic, and is selected based on the specific application and desired durability. By sealing gaps with caulk, you can enhance HVAC efficiency and reduce energy waste.
3.5 Door and Window Sealing
Doors and windows are common areas for air leaks, which can significantly impact HVAC efficiency. Proper sealing around doors and windows helps to eliminate drafts, prevent air infiltration, and reduce heat loss or gain. Adding door sweeps, installing window films, or using draft stoppers can all contribute to improved sealing and enhanced energy efficiency.
3.6 Chimney Sealing
If you have a chimney, it is crucial to ensure that it is properly sealed when not in use. Chimneys can be a significant source of air leaks, allowing conditioned air to escape and outdoor air to infiltrate the living space. Installing a chimney balloon or airtight damper can help to seal the chimney when it is not in use, preventing unnecessary energy losses and maintaining indoor comfort.
3.7 Pipe and Conduit Sealing
Pipes and conduits that pass through walls, floors, or ceilings can create avenues for air leakage if not properly sealed. Applying insulation and sealant around these penetrations helps to prevent air infiltration and maintain consistent indoor temperatures. By sealing pipe and conduit penetrations, you can enhance HVAC efficiency and reduce energy waste.
3.8 Electrical Outlet Sealing
Electrical outlets and switches can contribute to air leaks in walls if not adequately sealed. Foam gaskets or outlet sealers can be installed behind outlet and switch plates to reduce drafts and improve energy efficiency. By addressing these often-overlooked areas, you can enhance the overall sealing of your building envelope and optimize HVAC performance.
3.9 Insulating Exterior Walls
In addition to insulating the walls, it is crucial to consider insulating the exterior walls to ensure optimal HVAC efficiency. Exterior wall insulation can be achieved through various methods, such as insulation boards, blown-in insulation, or insulated sheathing. By insulating the exterior walls, you can reduce heat transfer through the building envelope, enhance energy efficiency, and improve indoor comfort.
3.10 Properly Sealing Attics and Basements
Attics and basements are notorious for air leaks and insufficient sealing, making them prime areas for energy losses. Properly sealing attics and basements involves a combination of insulation, air sealing, and addressing any gaps or cracks. By ensuring that these spaces are effectively sealed, you can prevent uncontrolled air movement, improve energy efficiency, and create a more comfortable living environment.

This image is property of greenteamli.com.
4. The Impact of Poor Insulation on HVAC Efficiency
When insulation is inadequate or improperly installed, it can have several negative consequences on HVAC efficiency. Understanding the potential impacts can help you recognize the importance of proper insulation and the need for timely upgrades or repairs. Here are some of the effects of poor insulation on HVAC efficiency:
4.1 Increased Energy Consumption
One of the most noticeable impacts of poor insulation on HVAC efficiency is increased energy consumption. When there are gaps, cracks, or inadequate insulation in the building envelope, conditioned air escapes, and outdoor air infiltrates the living space. This forces the HVAC system to work harder to compensate for the energy losses, consuming more electricity or fuel in the process. Increased energy consumption leads to higher utility bills and unnecessary strain on the HVAC equipment.
4.2 Uneven Temperature Distribution
Poor insulation can result in uneven temperature distribution throughout your home or building. Inadequate insulation or air leaks can create hot or cold spots, where the temperature differs significantly from the desired set point. This can lead to discomfort, as some areas may feel too warm while others remain chilly. Uneven temperature distribution also indicates HVAC inefficiency, as the system struggles to maintain a consistent and comfortable indoor environment.
4.3 Overworked HVAC Equipment
When insulation is lacking or ineffective, HVAC equipment has to work overtime to compensate for energy losses. Inadequate insulation forces the heating or cooling system to operate at maximum capacity for extended periods, leading to increased wear and tear. Overworked HVAC equipment is more prone to breakdowns, malfunctions, and reduced lifespan. Poor insulation places excessive strain on the system, shortening its operational efficiency and requiring frequent repairs or premature replacements.
4.4 Reduced Indoor Air Quality
Proper insulation not only helps with temperature control but also contributes to maintaining good indoor air quality. Inadequate insulation can allow outdoor pollutants, allergens, and contaminants to infiltrate the living space. Additionally, poor insulation may create condensation or moisture issues, leading to the growth of mold, mildew, or bacteria. These factors can degrade indoor air quality, posing health risks and exacerbating respiratory conditions. Proper insulation helps to create a healthier living environment by minimizing the entry of pollutants and controlling moisture levels.
4.5 Higher HVAC Maintenance and Repair Costs
When a building lacks proper insulation, the HVAC system often experiences more frequent breakdowns, malfunctions, and performance issues. This increases the need for maintenance and repairs, adding to the overall costs of HVAC ownership. Inadequate insulation exposes the equipment to unnecessary stress, causing components to work harder and increasing the likelihood of failures. Regular maintenance may not be sufficient in addressing the issues caused by poor insulation, resulting in additional repair expenses.
4.6 Shortened HVAC System Lifespan
HVAC systems are designed to operate within a specified range of conditions, including proper insulation levels. When the insulation is insufficient, HVAC equipment is subjected to excessive workload and wear, significantly shortening its expected lifespan. Premature failure of critical components, such as compressors or heat exchangers, can occur due to the increased strain caused by poor insulation. By investing in proper insulation, you can extend the life of your HVAC system and avoid the costs associated with premature replacements.
4.7 Difficulty Meeting Temperature Settings
Poor insulation hampers the ability of the HVAC system to achieve and maintain the desired temperature set points. Inadequate insulation allows conditioned air to escape and outdoor air to infiltrate, making it challenging for the system to reach the desired indoor temperatures efficiently. As a result, the HVAC system may run continuously or struggle to keep up, leading to discomfort and dissatisfaction. Consistently failing to meet temperature settings also indicates inefficiency and the need for insulation improvements.
4.8 Potential Mold and Mildew Growth
Insufficient insulation can create conditions conducive to mold and mildew growth. When warm, moist air comes into contact with cooler surfaces due to inadequate insulation, condensation may occur. This moisture buildup can lead to mold and mildew growth, posing health risks and potentially damaging the building materials. Mold and mildew infestations can be challenging and costly to remediate, requiring professional intervention and possible structural repairs. Proper insulation helps to control moisture levels, minimizing the risk of mold and mildew development.
4.9 Inadequate Noise Control
Insulation also plays a role in noise control within a building. Poor insulation can allow external noises, such as traffic or neighbors, to infiltrate the living space, causing disturbances and reducing comfort. Additionally, inadequate insulation may lead to sound transmission within the building, resulting in the transfer of noise between rooms or floors. By upgrading and improving insulation, you can enhance noise control, creating a quieter and more peaceful indoor environment.
4.10 Negative Environmental Consequences
In addition to the direct impact on HVAC efficiency and indoor comfort, poor insulation has negative consequences for the environment. Inadequate insulation leads to increased energy consumption, which in turn increases the demand for electricity or fossil fuels. This reliance on non-renewable energy sources contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and environmental degradation. By improving insulation and reducing energy waste, individuals can play a crucial role in mitigating climate change and protecting the planet.

This image is property of greenteamli.com.
5. Benefits of Proper Insulation and Sealing in HVAC Efficiency
Understanding the importance of proper insulation and sealing in HVAC efficiency highlights the numerous benefits that homeowners and building occupants can enjoy. By investing in insulation and sealing improvements, you can unlock the following advantages:
5.1 Energy Savings
One of the most significant benefits of proper insulation and sealing is the potential for energy savings. By reducing heat loss and gain, preventing air leaks, and creating an efficient building envelope, you can significantly decrease the energy required to heat or cool indoor spaces. As a result, you can enjoy lower utility bills, maximizing the financial savings while minimizing your environmental impact.
5.2 Improved Indoor Comfort
Proper insulation and sealing contribute to enhanced indoor comfort by reducing temperature fluctuations, drafts, and cold spots. By creating a thermal envelope that effectively separates outdoor and indoor environments, you can maintain consistent and comfortable indoor temperatures throughout the year. Improved indoor comfort leads to increased satisfaction and well-being for occupants, allowing them to fully enjoy their living or working spaces.
5.3 Longevity of HVAC Equipment
Investing in proper insulation and sealing can significantly extend the lifespan of your HVAC equipment. By reducing the workload on your systems and minimizing unnecessary strain, you can mitigate wear and tear, preserving the efficiency and functionality of the equipment for longer periods. By maximizing the lifespan of your HVAC systems, you can avoid premature replacements and reduce the associated costs.
5.4 Enhanced Indoor Air Quality
Proper insulation and sealing help to create a healthier indoor environment by minimizing the entry of outdoor pollutants, allergens, and contaminants. Additionally, by controlling moisture levels and preventing condensation, insulation plays a crucial role in preventing mold and mildew growth, which can have adverse effects on indoor air quality. Improved indoor air quality contributes to the well-being and respiratory health of occupants, promoting a healthier and more pleasant living or working environment.
5.5 Reduced Maintenance and Repair Costs
By investing in proper insulation and sealing, you can reduce the need for frequent maintenance and repairs. Adequate insulation and sealing minimize the strain on HVAC equipment, preventing excessive wear and component failures. As a result, you can save on maintenance and repair costs, as well as avoid the inconveniences associated with unexpected breakdowns. Timely insulation upgrades and sealing improvements can provide long-term cost savings and peace of mind.
5.6 Increased Environmental Sustainability
Efficient insulation and sealing contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions. By minimizing the demand for non-renewable energy sources, individuals can play a significant role in combating climate change and environmental degradation. Investing in proper insulation and sealing is a proactive and responsible step towards reducing your carbon footprint and promoting a more sustainable future.
5.7 Noise Reduction
In addition to thermal benefits, insulation can improve noise control within a building. Proper insulation helps to reduce exterior noise infiltration, creating a quieter indoor environment. Additionally, insulation improves soundproofing between rooms or floors, creating a more peaceful and tranquil living or working space. Enhanced noise reduction contributes to overall comfort and well-being, allowing occupants to focus, relax, and enjoy their surroundings.
5.8 Enhanced Home Value
Proper insulation and sealing can have a positive impact on the value of your property. Energy-efficient homes with effective insulation and sealing are in high demand among buyers due to the associated benefits, such as reduced utility bills and greater indoor comfort. Investing in insulation upgrades and sealing improvements can increase your home’s attractiveness to potential buyers, making it a valuable and desirable asset in the real estate market.
5.9 Compliance with Building Codes
Proper insulation and sealing are essential for meeting building code requirements in many regions. Building codes often stipulate minimum insulation levels and specifications to ensure energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and environmental responsibility. By upgrading your insulation and sealing to meet or exceed these requirements, you can ensure compliance with local regulations and avoid potential penalties or restrictions.
5.10 Positive Impact on Health and Well-being
The benefits of proper insulation and sealing extend beyond energy efficiency and comfort – they also have a positive impact on health and well-being. By improving indoor air quality, reducing the presence of allergens and pollutants, and creating a quieter living or working environment, you can enhance overall occupant health, productivity, and quality of life. Adequate insulation and sealing contribute to a healthier living space, supporting physical and mental well-being.
In conclusion, the role of insulation and sealing in HVAC efficiency cannot be overstated. Adequate insulation helps reduce heat loss and gain, improve energy efficiency, enhance indoor comfort, increase equipment lifespan, lower energy bills, and minimize environmental impact. Choosing the right insulation type for your specific needs and properly sealing your building envelope are essential steps in optimizing HVAC efficiency and reaping the numerous benefits associated with proper insulation and sealing. By investing in insulation upgrades and sealing improvements, you can create a comfortable, energy-efficient, and sustainable living or working environment while maximizing the performance and longevity of your HVAC systems.
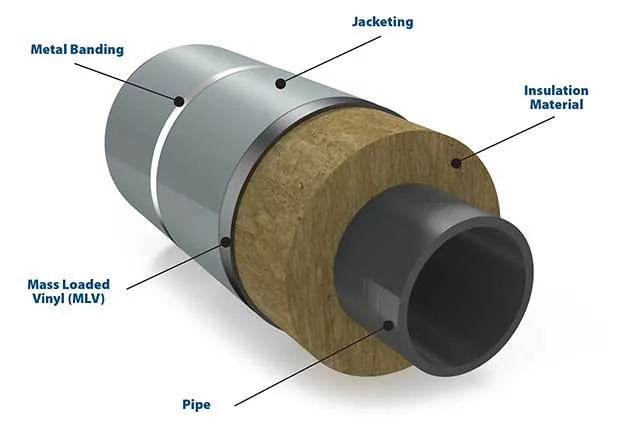
This image is property of hvac-eng.com.

