
HVAC Services
Get Professional Repairs From The Area's Trusted HVAC Technicians. Ask About Our Services! We Offer Professional Heating & Cooling System Repairs And Guarantee Long-Lasting Results.
Got Question? Call us: (850) 678-2665Financing
Introduction to HVAC Systems
Learn the basics of HVAC systems with this informative post. Understand the components, purpose, types, energy efficiency, and maintenance. Gain insights from the leader in HVAC service repair and maintenance.
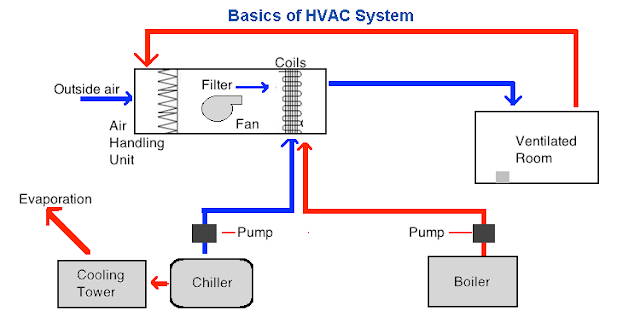
In this article, we’ll provide you with a brief introduction to HVAC systems. If you’ve ever wondered how your home or office stays cool in the summer and warm in the winter, HVAC is the answer. HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning, and it’s responsible for creating a comfortable indoor environment. Whether you’re in Niceville, FL, or the surrounding area, Tempacure Heating and Air Conditioning is the company to call for all your HVAC needs. With their expertise in HVAC service repair and maintenance, they’ve earned the reputation of being the leader in this field. So, let’s get started and learn the basics of HVAC systems.
This image is property of www.indiastudychannel.com.
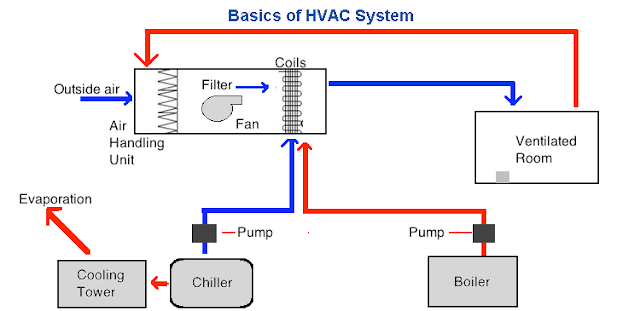
Basics of HVAC Systems
Welcome to the world of HVAC systems! Whether you’re a homeowner looking to improve your indoor comfort or a business owner in need of a reliable heating and cooling solution, understanding the basics of HVAC systems is essential. In this article, we will explore the definition of HVAC, its components, purpose, types, energy efficiency, choosing the right system, common issues, and the importance of regular maintenance and repair.
What is HVAC?
Definition of HVAC
HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. It refers to the technology used for indoor environmental comfort. An HVAC system is designed to control the temperature, humidity, and air quality in a closed space, be it a home, office, or commercial building. By regulating these factors, HVAC systems ensure optimal comfort and a healthy living or working environment.
Explanation of HVAC Acronym
The acronym HVAC stands for the following:
- Heating: This component provides warmth to the indoor space during cold weather. It can be achieved through various methods such as furnaces, heat pumps, or electric heaters.
- Ventilation: Ventilation systems ensure the circulation of fresh air and the removal of stale air, odors, and pollutants from the indoor space. It helps maintain good indoor air quality.
- Air Conditioning: Air conditioning is responsible for cooling and dehumidifying the indoor air during hot weather. It enhances comfort by providing a pleasant temperature.
- HVAC systems combine these three components to create a comfortable and healthy indoor environment.
Components of an HVAC System
To better understand how HVAC systems work, let’s take a closer look at their primary components:
Heating
Heating is a crucial component of HVAC systems, especially in colder climates. It provides warmth to the indoor space by using various equipment such as furnaces, boilers, or heat pumps. These systems generate heat and distribute it throughout the building.
Ventilation
Ventilation plays a vital role in maintaining indoor air quality. It involves the exchange of outdoor and indoor air to ensure the removal of pollutants, odors, and excess moisture. Ventilation systems can be natural, mechanical, or a combination of both.
Air Conditioning
Air conditioning is responsible for cooling the indoor air and maintaining a comfortable temperature during hot weather. It removes heat and moisture from the indoor space through a refrigeration cycle, creating a pleasant and cool environment.
Thermostat
The thermostat acts as the control center of an HVAC system. It allows you to set and adjust the desired temperature, controlling the heating and cooling cycles. Modern thermostats come with programmable features, enabling you to customize temperature settings based on your schedule and preferences.
Ductwork
Ductwork refers to the network of channels that distribute heated or cooled air throughout the building. It consists of a series of interconnected pipes, vents, and registers that ensure the efficient flow of air. Properly designed and sealed ductwork is essential for optimal HVAC system performance.
Purpose of HVAC Systems
Now that we understand the components, let’s delve into the purpose of HVAC systems:
Maintaining Comfortable Indoor Temperatures
One of the primary purposes of HVAC systems is to ensure comfort by regulating indoor temperatures. During the cold winter months, heating systems keep your home warm and cozy, while air conditioning systems provide relief from the scorching summer heat.
Improving Indoor Air Quality
Good air quality is vital for our health and well-being. HVAC systems help improve indoor air quality by filtering out pollutants, dust, allergens, and other harmful particles. Proper ventilation and air purification systems ensure the circulation of fresh and clean air, reducing the risk of respiratory issues and allergies.
Controlling Humidity Levels
Excessive humidity can lead to discomfort, mold growth, and damage to furniture and belongings. HVAC systems control humidity levels by removing excess moisture from the air during the cooling process. This feature is particularly important in humid climates.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a critical aspect of HVAC systems. By using energy-efficient components and technologies, these systems can reduce energy consumption while still providing optimal comfort. High-efficiency HVAC systems help lower utility bills and contribute to a sustainable environment.
Ensuring Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation is essential for maintaining a healthy indoor environment. HVAC systems ensure adequate ventilation by exchanging fresh outdoor air with stale indoor air. This process helps remove odors, pollutants, and humidity while providing sufficient oxygen supply.
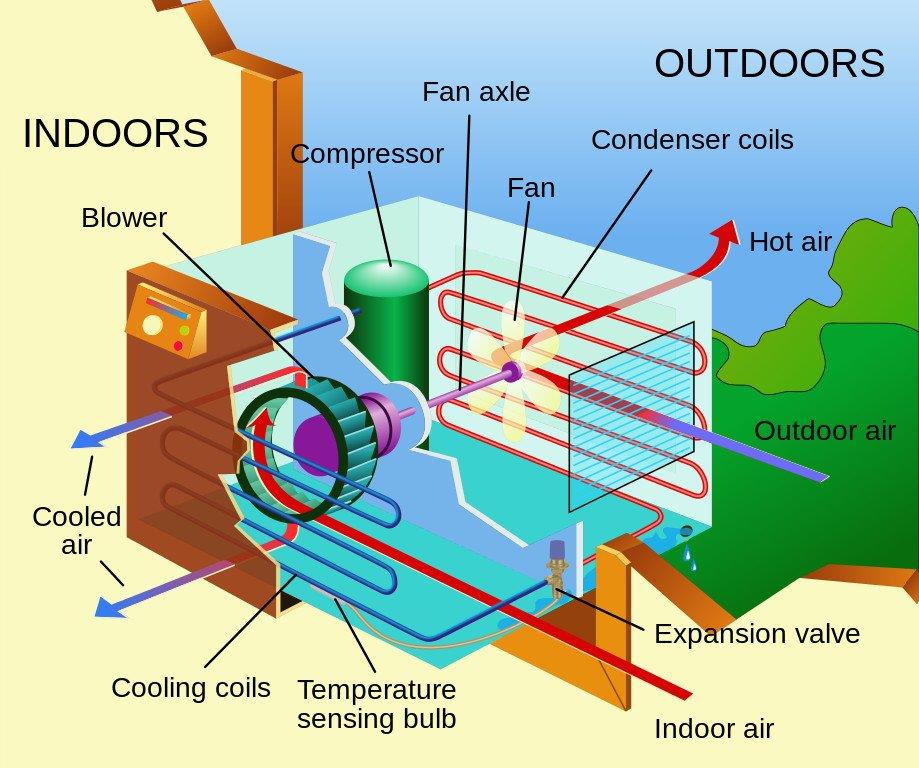
This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Types of HVAC Systems
There are several types of HVAC systems available, each suited for different environments and needs. Let’s explore some of the most common types:
Split System
The split system is the most traditional and widely used HVAC system. It consists of an indoor unit containing the evaporator coil and an outdoor unit housing the condenser coil. The two units work together to heat or cool the indoor space.
Packaged System
The packaged system is commonly used in small commercial buildings or homes without sufficient indoor space. In this system, all components, including heating, cooling, and ventilation, are contained in a single unit installed outdoors.
Ductless Mini-Split System
Ductless mini-split systems are an excellent option for buildings without existing ductwork. They consist of an outdoor unit connected to one or more indoor units via refrigerant lines. These systems provide zoned heating and cooling, allowing for individual temperature control in different areas or rooms.
Geothermal Heating and Cooling System
Geothermal systems use the constant temperature of the ground to provide heating and cooling. These systems utilize a series of underground pipes filled with a water-based solution to transfer heat to or from the ground, depending on the season.
Hybrid Heat Pump System
Hybrid heat pump systems combine the benefits of a heat pump and a furnace. They automatically switch between electric heating and gas heating based on outdoor temperatures and energy costs, providing an efficient and cost-effective solution.
Energy Efficiency in HVAC Systems
Energy efficiency is a significant consideration when choosing an HVAC system. Efficient systems not only reduce energy consumption but also save money on utility bills. Let’s explore some key aspects of Energy Efficiency in HVAC Systems:
Energy Efficiency Ratings
HVAC systems are assigned energy efficiency ratings to help consumers make informed decisions. These ratings indicate the system’s efficiency in converting energy into heat or cooling power. The higher the rating, the more efficient the system.
SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio)
SEER is a rating used to measure the cooling efficiency of air conditioning systems. It represents the ratio of cooling output to energy input. A higher SEER rating signifies a more energy-efficient system.
AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency)
AFUE measures the efficiency of heating systems, particularly furnaces. It represents the ratio of heat output to energy input. Higher AFUE ratings indicate more efficient heating systems that convert more energy into usable heat.
ENERGY STAR Certification
ENERGY STAR is a program by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) that promotes energy efficiency. HVAC systems with an ENERGY STAR certification are independently tested and meet strict energy efficiency guidelines, ensuring long-term savings and reduced environmental impact.
Tips for Improving Energy Efficiency
There are several steps you can take to improve the energy efficiency of your HVAC system:
- Regularly clean and replace air filters to ensure optimal airflow.
- Properly seal and insulate your home to prevent air leakage.
- Install a programmable thermostat to customize temperature settings based on your schedule.
- Schedule regular maintenance to keep your system running efficiently.
- Consider upgrading to a high-efficiency HVAC system.
This image is property of www.indiastudychannel.com.
Choosing the Right HVAC System for Your Needs
Choosing the right HVAC system requires careful consideration of various factors. Let’s explore some key considerations to help you make an informed decision:
Considerations for Residential vs. Commercial Buildings
Residential and commercial buildings have different requirements when it comes to HVAC systems. Residential systems are typically smaller and focus on individual comfort, while commercial systems must accommodate larger spaces and a higher number of occupants.
Sizing and Load Calculation
Proper sizing of an HVAC system is crucial for optimal performance. An oversized system leads to frequent cycling, energy waste, and decreased comfort, while an undersized system may struggle to adequately heat or cool the space. Conducting a load calculation helps determine the appropriate system size for your needs.
Budgetary Constraints
Budget is an important consideration when selecting an HVAC system. It’s essential to find a balance between upfront costs and long-term energy savings. High-efficiency systems may have a higher initial cost but can result in significant energy savings over time.
Climate and Region
The climate and region in which you live greatly influence the HVAC system you choose. Cold climates require efficient heating systems, while hot and humid regions necessitate powerful air conditioning units. Considering the specific requirements of your climate will ensure optimal comfort throughout the year.
Environmental Impact
In today’s environmentally conscious world, considering the environmental impact of your HVAC system is crucial. Look for systems that use eco-friendly refrigerants and have high energy efficiency ratings. Investing in a system with a lower carbon footprint not only benefits the environment but also contributes to a sustainable future.
Common HVAC System Issues
While HVAC systems are designed to provide reliable performance, issues can sometimes arise. Here are some common problems encountered with HVAC systems:
Poor Air Flow
Poor air flow can result from clogged or dirty air filters, blocked vents, or ductwork issues. This problem reduces the system’s efficiency and may lead to inconsistent temperatures.
Inconsistent Temperatures
If you notice that certain areas in your home or building are significantly warmer or cooler than others, it may indicate an issue with the HVAC system. Inconsistent temperatures can result from faulty thermostats, ductwork leaks, or improper system balancing.
Air Leakage
Air leakage occurs when there are cracks or gaps in the ductwork, causing conditioned air to escape. This problem not only affects comfort but also wastes energy, leading to higher utility bills.
Refrigerant Leaks
Refrigerant leaks can occur in air conditioning systems, resulting in reduced cooling capacity and potential environmental harm. Low refrigerant levels can cause the system to work harder, leading to higher energy consumption.
Thermostat Malfunctions
Thermostats control the heating and cooling cycles of an HVAC system. Malfunctioning thermostats may lead to inaccurate temperature readings or a failure to activate the heating or cooling components.

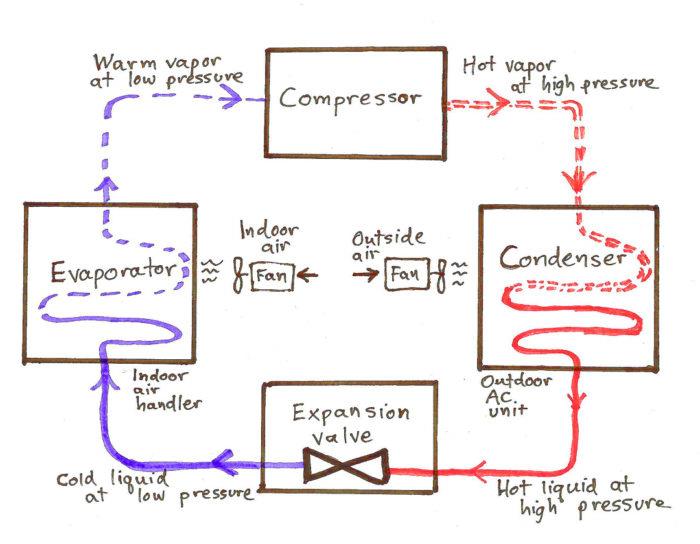
This image is property of image.slidesharecdn.com.
Regular Maintenance and Repair
Regular maintenance and timely repairs are essential for the optimal performance and longevity of your HVAC system. Here’s why:
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Routine maintenance helps prevent system breakdowns, improve energy efficiency, and extend the lifespan of your HVAC system. It involves tasks such as cleaning or replacing air filters, inspecting electrical connections, lubricating moving parts, and checking refrigerant levels.
Common Maintenance Tasks
Some common maintenance tasks for HVAC systems include:
- Cleaning or replacing air filters.
- Checking and tightening electrical connections.
- Lubricating moving parts, such as motors and fans.
- Inspecting ductwork for leaks or damage.
- Testing thermostat functionality.
- Cleaning condenser and evaporator coils.
- Checking refrigerant levels and inspecting for leaks.
Signs for HVAC Repair
Recognizing signs that your HVAC system requires repair is crucial to avoid further damage and costly replacements. Some common signs to watch out for include:
- Unusual noises, such as grinding or banging sounds.
- Inconsistent or insufficient heating or cooling.
- Frequent system cycling or short-cycling.
- Rapid or unusual increase in energy bills.
- Strange odors coming from the system.
- System not turning on or off properly.
Finding a Reliable HVAC Service Provider
When it comes to maintenance and repairs, it’s vital to choose a reliable HVAC service provider. Look for a company with a good reputation, experienced technicians, and excellent customer reviews. Asking for recommendations from friends, family, or neighbors can also help you find a reputable provider.
Cost of Maintenance and Repair
The cost of HVAC maintenance and repair can vary depending on various factors, such as the complexity of the issue, system size, and location. It’s important to budget for regular maintenance and address repairs promptly to avoid more significant problems and expenses down the line.
Conclusion
HVAC systems play a significant role in ensuring indoor comfort and maintaining a healthy living or working environment. By understanding the basics of HVAC systems, you can make informed decisions when it comes to choosing, operating, and maintaining your system.
Continual advancements in HVAC technology provide more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly options. By opting for professional installation, regular maintenance, and timely repairs, you can enjoy optimal performance, energy savings, and a comfortable indoor environment for years to come. So, don’t neglect your HVAC system’s needs – it’s essential for your comfort and well-being!
This image is property of 1.bp.blogspot.com.




